Magenta SRL and MICC participated at the 16th edition of the International Conference on Image Analysis and Processing (ICIAP 2011) with a live demo of both off-line and on-camera traffic monitoring applications developed within the ORUSSI European Project.
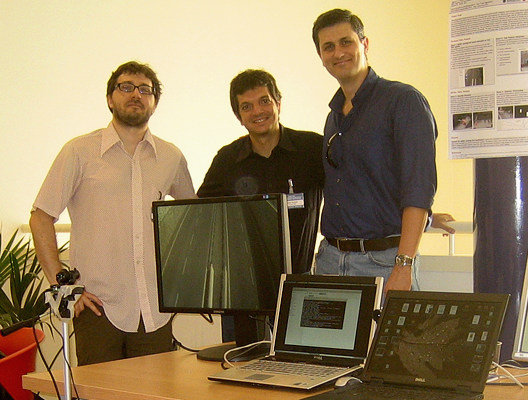

MICC and Magenta SRL demo at ICIAP 2011
ICIAP is organized every two years by the Italian group of researchers in pattern recognition (GIRPR), which is the Italian IAPR Member Society, with the aim to bring together researchers in image processing and pattern recognition from around the world. The 16th edition of the conference was organized by the University of Bologna, Ravenna site.
The main target of ICIAP 2011 was to provide a place in which the most recent approaches and goals in image analysis could be presented and discussed.
Main topics included:
- Image analysis and processing
- Pattern recognition and Vision
- Machine Learning and Multimedia
- Cultural Heritage and Applications
The demo by Magenta SRL and MICC presented an embedded solution for vehicle counting and speed estimation and off-site video analysis tools to detect anomalous behaviors and to perform semantic compression of videos. An on-camera application for extraction of FAST feature points was also shown.